Introduction
The medical gas pipeline system is one of the essential components in any modern healthcare facility, such as hospitals and medical centers. This network provides a range of vital gases used in daily medical care—including oxygen, nitrous oxide, medical air, vacuum (suction), carbon dioxide, and others—in a safe, organized manner, in compliance with international standards.
Importance of the Medical Gas Pipeline System
The medical gas pipeline plays a critical role in supporting medical and therapeutic procedures. Its main functions include:
- Enabling mechanical ventilation for patients in intensive care units or during surgical operations.
- Providing oxygen to patients suffering from respiratory conditions.
- Operating anesthesia equipment using nitrous oxide and other gases.
- Removing secretions and surgical waste through the central vacuum system.
- Ensuring a safe working environment for medical staff by controlling gas flow and reducing reliance on portable cylinders.
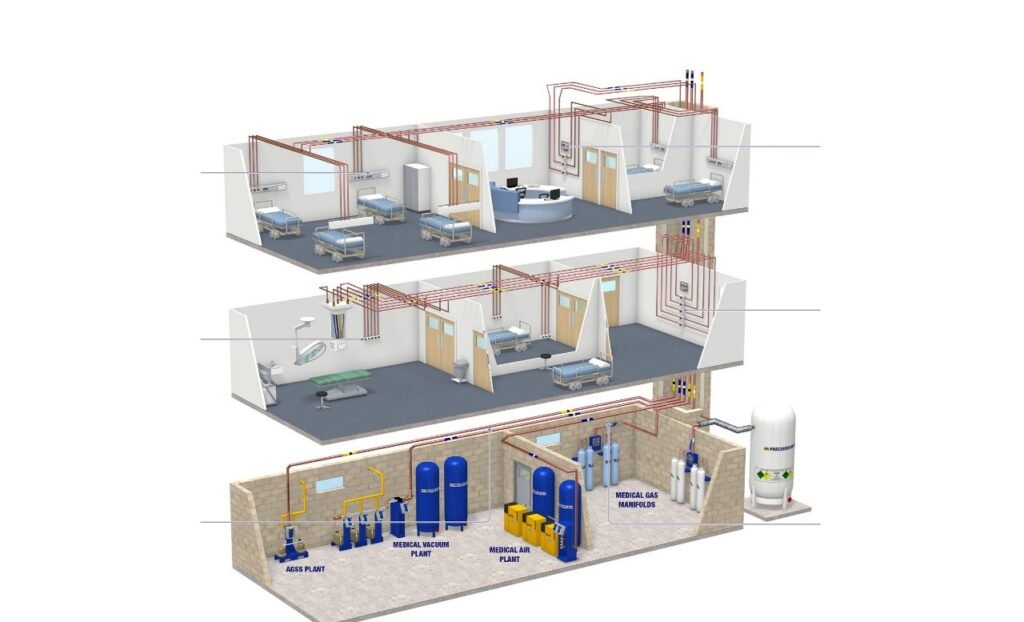
Components of the Medical Gas Pipeline System
Sources of Medical Gases:
- Central Storage Tanks: Used to store liquid oxygen or medical air.
- Compressed Cylinders: Serve as backup or emergency supply.
- Oxygen Generators: Devices that locally produce oxygen from ambient air.
Control and Regulation Units:
- Manifolds: Regulate gas flow from the source to the pipeline network.
- Safety and Control Valves: Ensure proper flow and prevent leaks.
Piping Network:
- Pipes made of copper or corrosion-resistant, high-pressure materials.
- The network extends through walls and ceilings to supply each point of use in different hospital departments.
Points of Use:
- Located in operating rooms, ICUs, emergency departments, and other clinical areas.
- Connected to medical equipment such as anesthesia machines, ventilators, and suction devices.
Types of Gases Used
| Gas | Use |
|---|---|
| Oxygen (O₂) | Respiratory support and oxygen therapy |
| Nitrous Oxide (N₂O) | Anesthetic gas for surgical procedures |
| Medical Air | Powering equipment and providing clean breathing air |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Used in certain surgical procedures like endoscopy |
| Vacuum (Suction) | Removal of fluids and secretions from the patient |
| Instrument Air | Operating pneumatic surgical instruments |
Safety and Design Standards
- The system must comply with standards such as NFPA 99 (USA) or HTM 02-01 (UK).
- Installation of alarm systems to monitor pressure and detect leaks.
- Regular maintenance and operation by certified technicians.
- Clear color coding and labeling to prevent gas mix-ups according to international guidelines.
Challenges and Considerations
- High cost of installation and maintenance.
- Need for specialized engineers to ensure proper operation.
- Backup systems must be available to prevent unexpected service interruptions.
- Future expansions should be anticipated during initial design.
Conclusion
The medical gas pipeline system is indispensable in the infrastructure of healthcare facilities. Its importance lies in its direct role in saving lives, facilitating surgeries, and delivering effective patient care. Therefore, its design, installation, and operation must follow the highest standards of quality and safety to ensure uninterrupted and reliable service.